How To Select And Change A Color In Photoshop
Today nosotros're going to look at three means to change colors in Adobe Photoshop. These tools are used to change the color of an object in a photograph or recolor a portion of an image.
Although Photoshop offers endless tools for correcting color or subtly toning an image, the techniques in this article are designed for the more specific and dramatic artistic outcome of completely irresolute the color of an object. These three methods are fairly singled-out and which technique is best is going to be completely dependent on the image yous are working with.
Below, I do my best to offer suggestions of which types of images each technique volition work with. Nonetheless, I recommend experimenting with them yourself to get a feel for what works best for you.

We're going to jump right into the steps below using layers, adjustment layers, and masking, and so if those terms aren't familiar to y'all, I recommend checking out the article that Spencer wrote on Photoshop Layers and Masking before we brainstorm.
Table of Contents
Changing Colors Using a Hue/Saturation Adjustment Layer
The start way to alter colors is past using the Hue/Saturation sliders. While this method has the potential of being the easiest way to change the colour of an object, it comes with a pretty big caveat: it doesn't work well in every epitome. Simply we're going to start with it because when it works, it's a very fast and like shooting fish in a barrel way to change colors.
Hue/Saturation works all-time when you have an epitome with really skilful color separation betwixt the color you want to change and the rest of the image. If your image is adequately monochromatic, or you have a lot of the aforementioned color throughout the prototype, irresolute the color of just i of those objects is going to be a chip trickier.
Using the Hue/Saturation slider is adequately straightforward. The Hue Slider is a bar-shaped representation of a colour wheel. When yous slide the hue slider, you are shifting all of the colors in your image around the color wheel. So, starting at the center the bar, yous can shift the slider upwards to 180 degrees in either management.
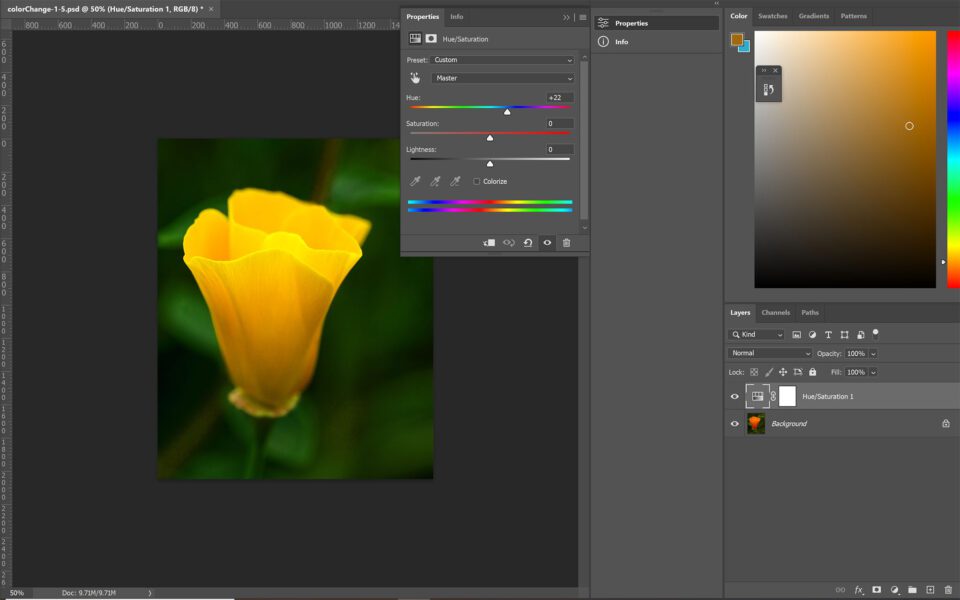
If you simply slide the hue slider, you are making global adjustments- significant you are irresolute every color in your image. This tool becomes much more useful and more than practical when you apply the dropdown menu, or the ii rainbow sliders at the lesser of the Hue/Saturation panel, to limit the range of the adjustments you are making. Y'all can see that change below:
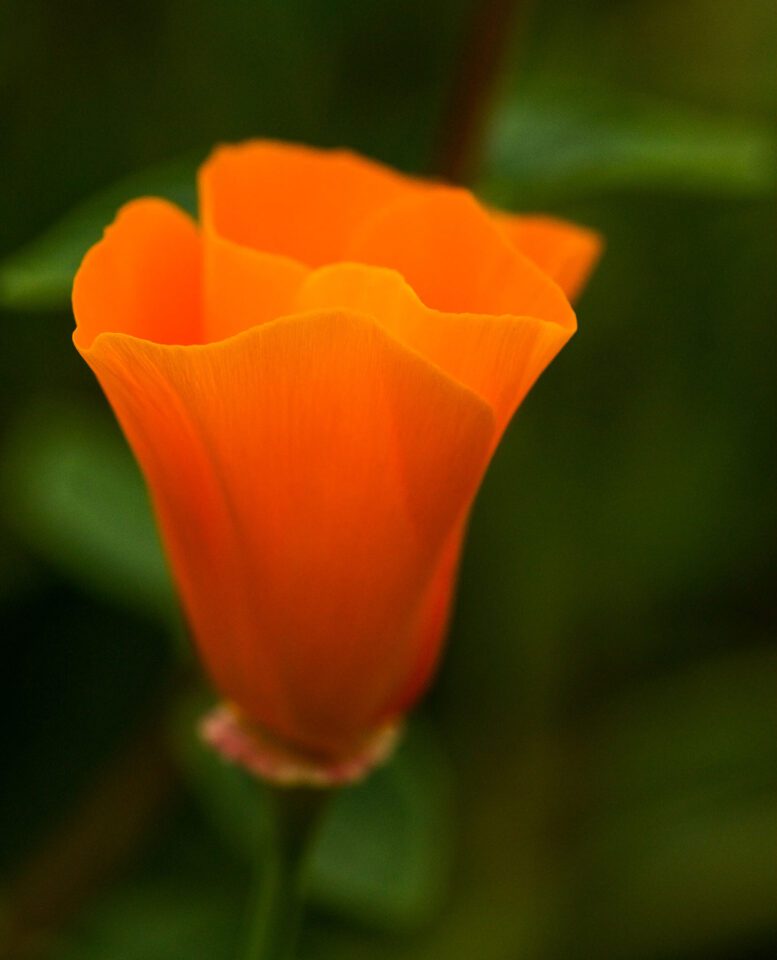
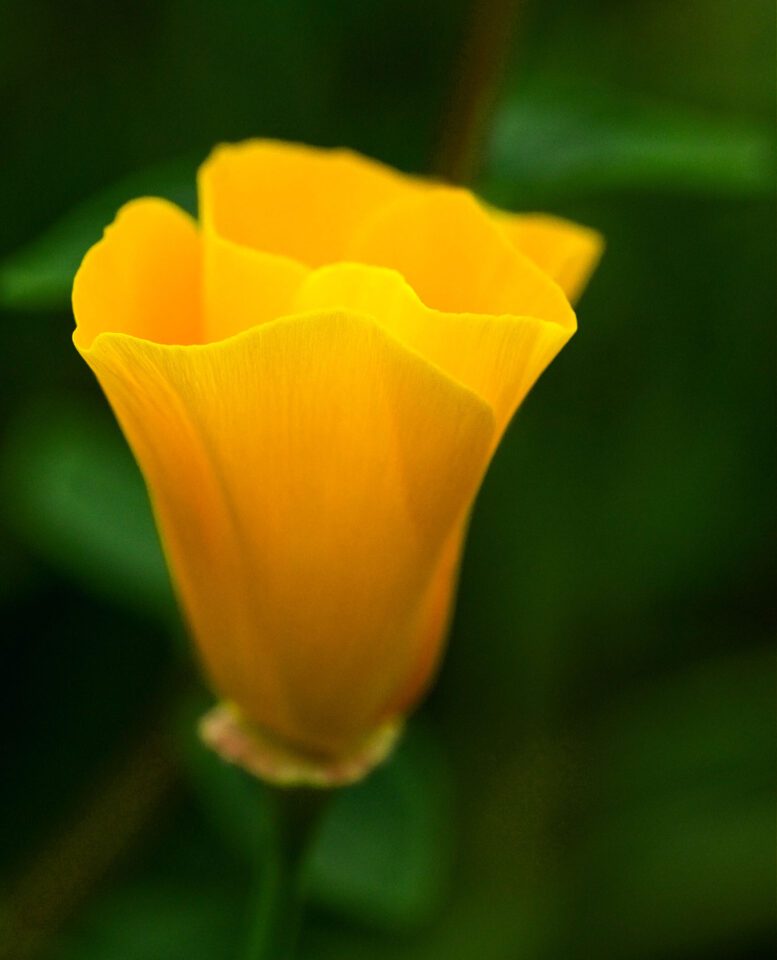


This technique can as well exist combined with masking, which makes it even more powerful. (Though when an image needs more than a bones mask, I usually prefer to use the other 2 techniques that I'll cover in a moment.)
Aside from the simple quickness of this technique, another major benefit is that it's already not-destructive by default. Since y'all are working with an adjustment layer, y'all tin go dorsum and change the color as many times equally you want.
However, a drawback is that it tin shift some colors or areas of the image that you lot didn't intend. In the example in a higher place, y'all volition run across that fifty-fifty though the flower is what inverse colors the about, the background also shifted a bit. You can minimize this by using the two rainbow sliders at the bottom of the Hue/Saturation panel to limit the colors that are adjusted, but yous may not be able to eliminate it completely. In this particular instance, the color shift worked, so I just left information technology. If it had bothered me I could have used a layer mask to "erase" the colour change anywhere I didn't want it.
Here's another example. The following is the original prototype:
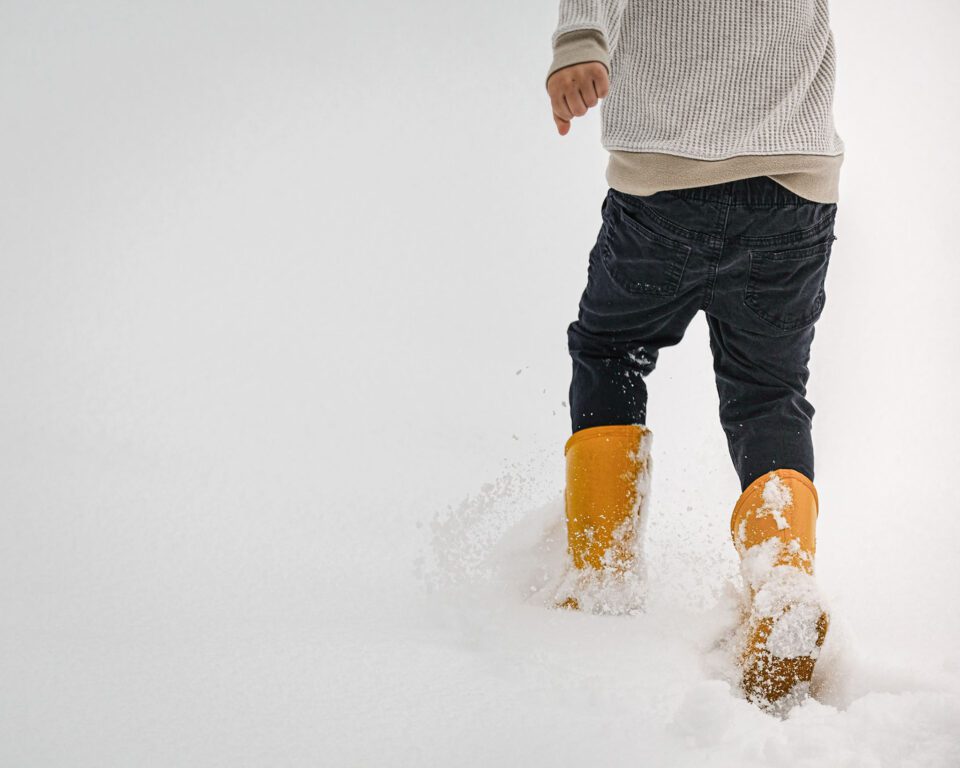

In this example, I used the fact that the Hue/Saturation Adjustment layer affects the unabridged image to my reward. You may notice in the paradigm above that there's a very subtle reflection of the yellow boots in the nearby snow. Reflections and color casts on surrounding objects are something you want to watch out for when changing colors. In this case, the Hue/Saturation adjustment made that easy, as you can come across below:
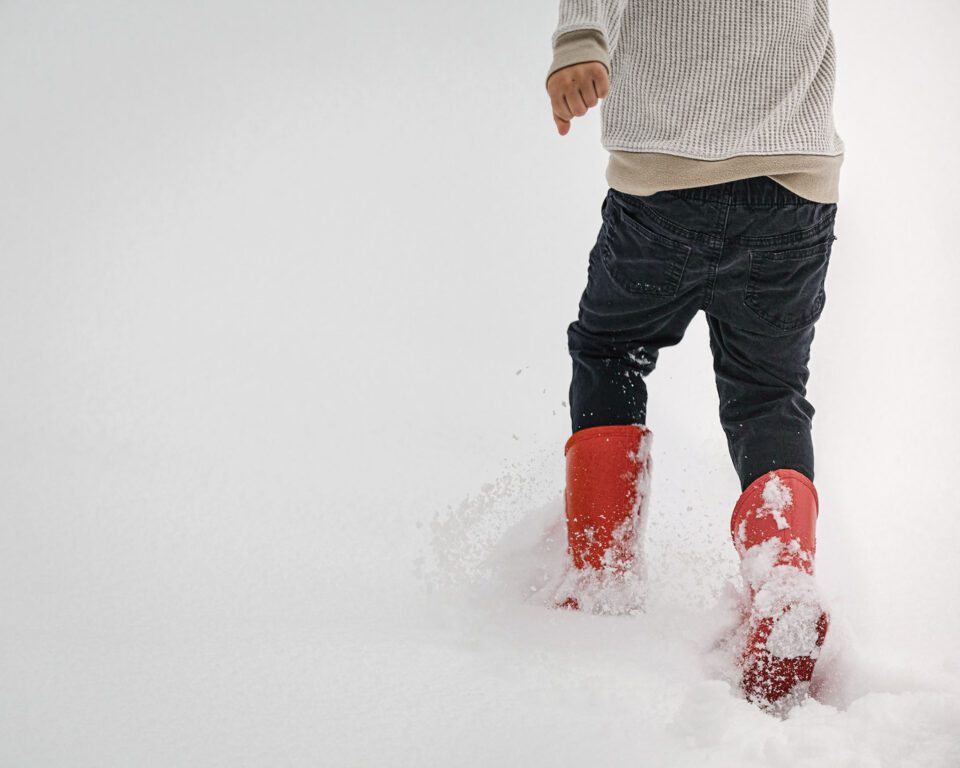

However, I did need to apace mask over the hand and the shirt, which also had some yellow in them, to get rid of the unwanted red color change in those areas. Information technology was all the same a very quick and easy edit overall, though.
Changing Colors Using Blending Modes
Blending modes are an extremely powerful part of layers in Photoshop. Today we're going to await at the 2 blending modes that tin help u.s.a. re-color an object in an image, simply for a wait at what the other blend modes can practise, cheque out this article on Blend Modes past Madhu.
To modify colors using blending modes, showtime past creating a blank layer in a higher place your original image. Change the blending way of the bare layer to either hue or saturation. These 2 modes are similar, only they do produce dissimilar effects. "Hue" keeps the saturation and luminosity of the original (underlying) layer while irresolute the hue to match your new color. "Color" changes both the colour and the saturation while retaining the original layer's luminosity. The difference may seem subtle, but it oftentimes has a substantial upshot on the image. Fortunately, it is piece of cake and non-subversive to toggle between the two blend modes to see what works in your image.
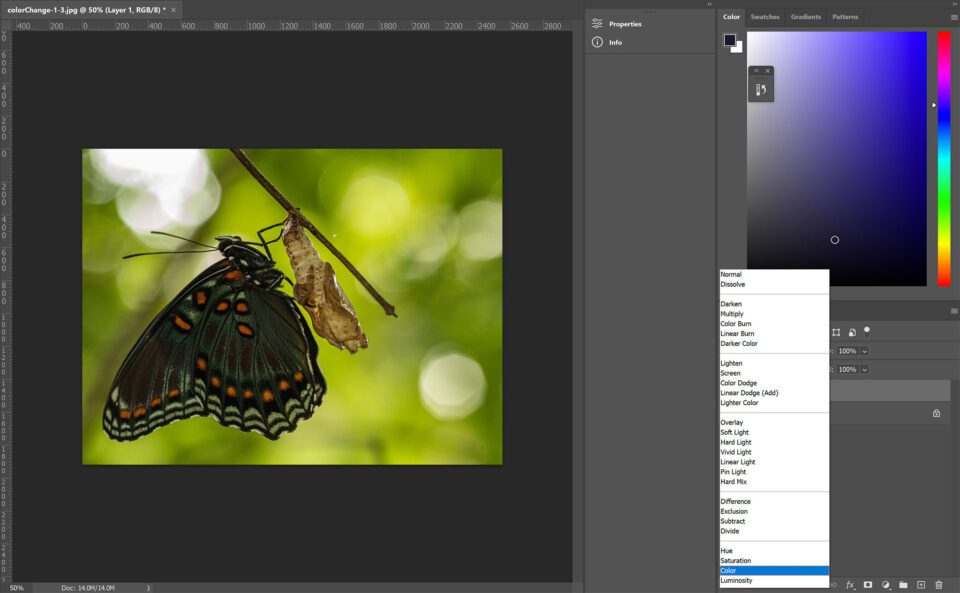
The next stride is to paint (on the new blank layer) over the portion of the prototype you desire to change with the brush tool and your chosen colour. If the epitome you are recoloring has articulate, singled-out outlines, and you are using a pen tablet to do your painting, and then painting might exist very straightforward. Just about of the time nosotros aren't quite that lucky! You tin can hands combine this technique with a layer mask, using any of Photoshop's masking options to create a layer mask on the new (hue or color) layer before painting.
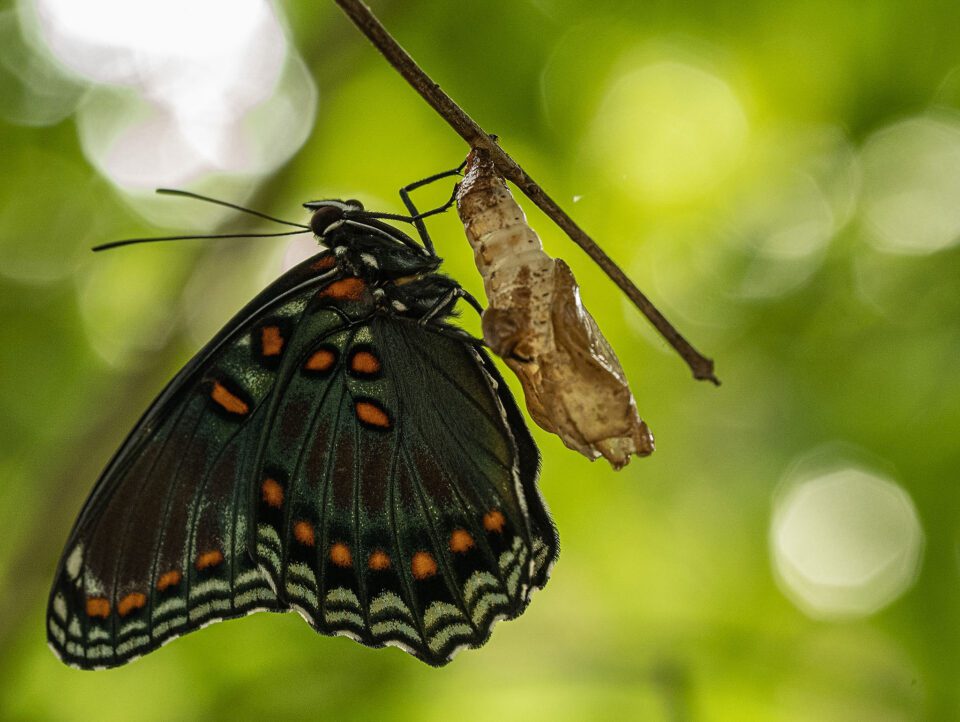
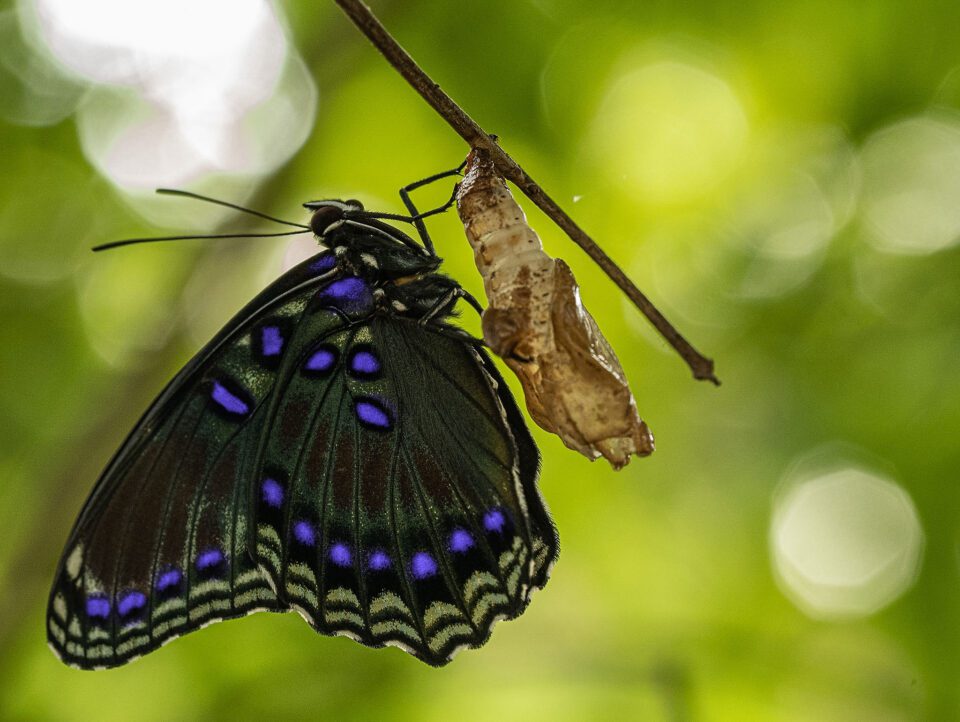


When you find yourself needing to add a layer mask to your hue/color layer, there are a few tips that often come in handy. The beginning is that after y'all've finished making your mask, you tin use a gaussian blur filter straight on the mask. This tin soften up the mask only enough to make the color modify appear more natural.
Also, the colour range tool (located under the "Select" carte at the height) sometimes works well for selecting the surface area yous want to recolor in the first place. The color range tool will select that same colour in other areas of the image as well (non different the Hue/Saturation aligning layer), simply if the other areas don't overlap/touch the area yous need to re-color, you can merely pigment over those portions of the image.
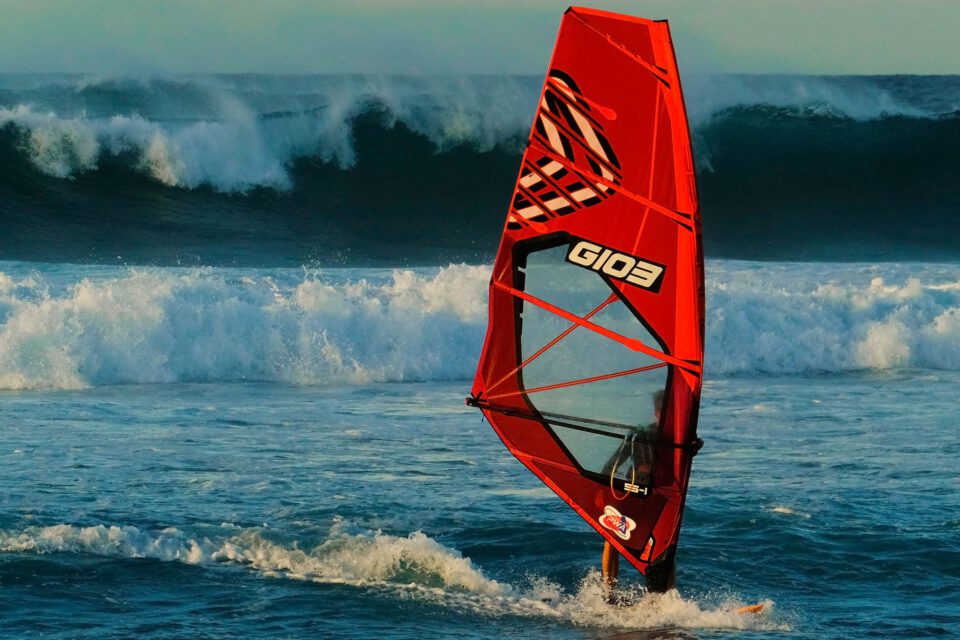
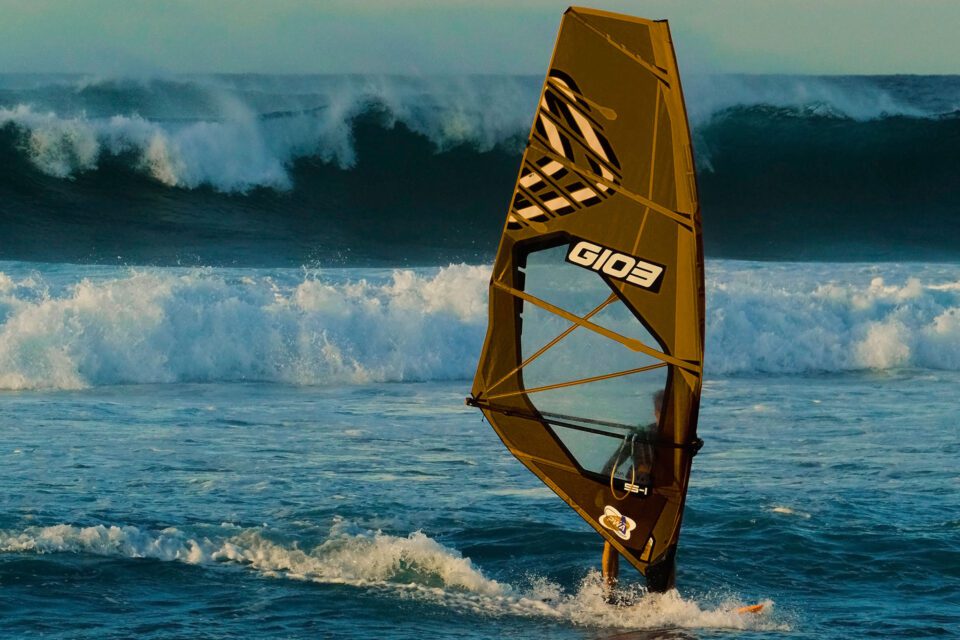


Changing Colour Using the Colour Replacement Brush
When y'all need to modify the colour of a more than complex expanse in a photo, something with smaller spaces, or less defined edges, the Colour Replacement Brush is your best choice. The Colour Replacement Brush is a very powerful tool subconscious under the regular Paint Brush Tool in Photoshop.
The Color Replacement Tool brings up a cursor that at beginning glance could exist confused with the typical castor. For years I really ignored this tool, assuming it was essentially the aforementioned as the in a higher place technique of using the brush with a colour or hue blending mode. Merely this tool is far more than powerful that it first appears and information technology contains some very useful controls that you volition find makes changing color far easier in many cases.

The general concept of using the Color Replacement Brush is fairly simple. As you paint over the object yous want to recolor, Photoshop will change only the colors that match whichever color is under the cantankerous-hair in the middle of the brush. It will supersede them with your called foreground color.
The actual painting technique is similar to using whatever Photoshop brush tool, although you want to make sure that the cantankerous-hair is always over the part of the image you lot want to recolor. Only while the concept is elementary, this tool contains many options that modify its behavior in dramatic and useful ways.

Mode
![]()
The mode selection hither works the aforementioned as changing the blending mode of the layer, similar we looked at before. You have the same Hue and Color options as well as Saturation (go on the hue and luminosity from the original color and replace only the saturation with the new color) and Luminosity (Keep the hue and saturation of the original color and adopt merely the luminosity from the new color). When you are using this tool for color replacement, you volition probably exist looking to use either the hue or color option.
Sampling Options
![]()
While these three options aren't labeled, the icons make sense once you empathize what they practise (and we will look at them in the guild they announced in the options bar). The sampling options control how Photoshop selects the color you will be replacing. With only i exception, the sampling is controlled by the cross-hair in the center of the brush cursor, but the sampling behavior changes depending on the choice selected.
The get-go pick is "Continuous," which continuously samples the colour nether the cross-pilus. As y'all move the brush tool, the cross-hair moves, and Photoshop is continuously updating the sampled color. (This option works well in near situations, especially when paired with the "detect edges" selection). It is of import when using this selection that you pay especially shut attending to the location of the cross-pilus every bit you lot paint.
The 2d pick is "Sample Once." It samples the color under the cross-hair once, when you lot offset click, and equally long every bit you continue to hold down your mouse button and paint information technology replaces only that one color that it originally sampled.
The 3rd option is the "Groundwork Color" selection and it replaces simply the colors that match whichever color is the background color swatch. This is the one option that does not use the cantankerous-hair for color choice, but honestly I accept never used information technology.
Limit
![]()
The "Limits" selection controls the behavior of the bodily painting/colour replacing that y'all do.
First, "Contiguous" is the default option, and it will simply supplant colors that both lucifer the sampled color (usually the color under the cantankerous-hair) and are adjacent to it, or touching it in some fashion. It will not supervene upon non-next pixels fifty-fifty if they are the sampled color and fall within the brush cursor area.
"Detect edges" works similar continuous but pays attention to the edges of an object and only replaces the colors that Photoshop identifies as being independent within those edges. While this does non work perfectly, particularly in areas with very complex or blurred edges, information technology works surprisingly well and makes recoloring quick and fairly straightforward, especially when paired with the continuous sampling option.
"Discontinuous" replaces the sampled color regardless of where it appears within the brush cursor area.
Tolerance
![]()
Tolerance controls how closely a colour must match the sampled colour in gild to be replaced. For images with only subtle variations in colors, yous will find that a low tolerance is necessary. If your object is not surrounded by like colors, you volition find that increasing the tolerance will work well and speed up your workflow. There is no magic formula to selecting the correct tolerance level; you will need to arrange it equally you lot go. If the replacement feels too particular, try increasing the tolerance. If it is non accurate plenty, subtract the tolerance. The tolerance has a surprisingly stiff effect on the way this tool works, so if the color replacement brush is not behaving the way y'all wait it to, the first matter to check is the tolerance level.
Putting Information technology Into Do
To apply the Colour Replacement Brush, select your desired new color as the foreground colour in the color swatches. Dissimilar the Adjustment layer technique and the Blending Mode technique above, when you utilize the Color Replacement Brush, you are working right on the original image layer – meaning that it's destructive. The fashion around this is to indistinguishable the layer and paint merely on the duplicate. That'due south ever practiced practice so that yous can disengage your piece of work if needed.
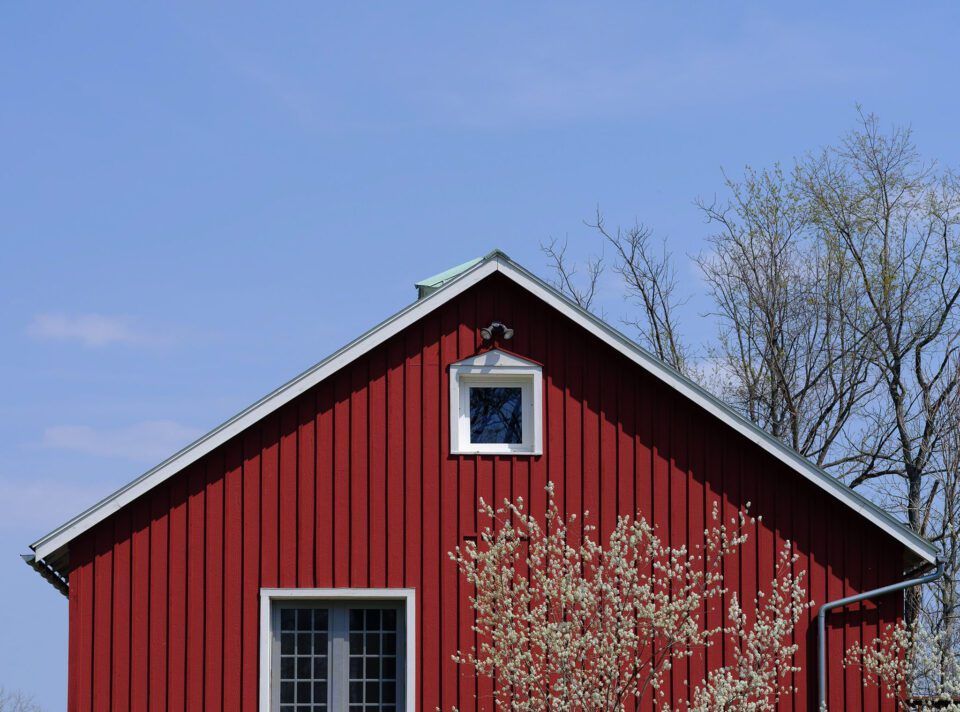

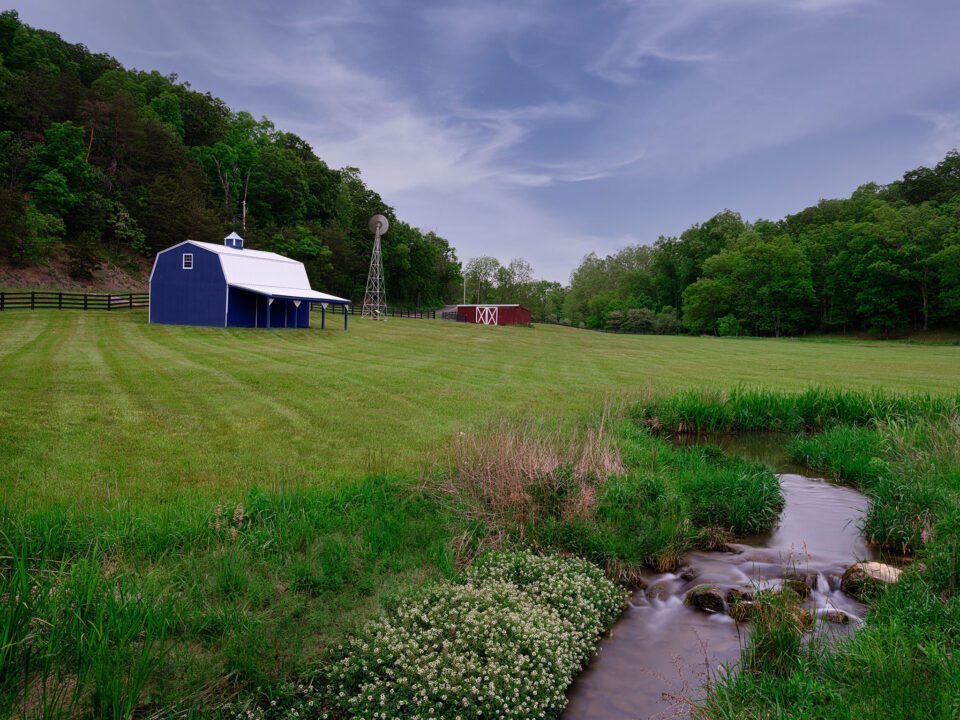
While the options in the colour replacement brush may seem overwhelming, I recommend starting with the sampling mode set to "Continuous" and the limit set to either "Face-to-face" or "Find Edges." A tolerance in the 50-lx percentage range is a adept starting point too. Every bit you begin to utilise the brush and experience its behavior, yous will get a feel for when you demand to adapt the settings and use other options instead.
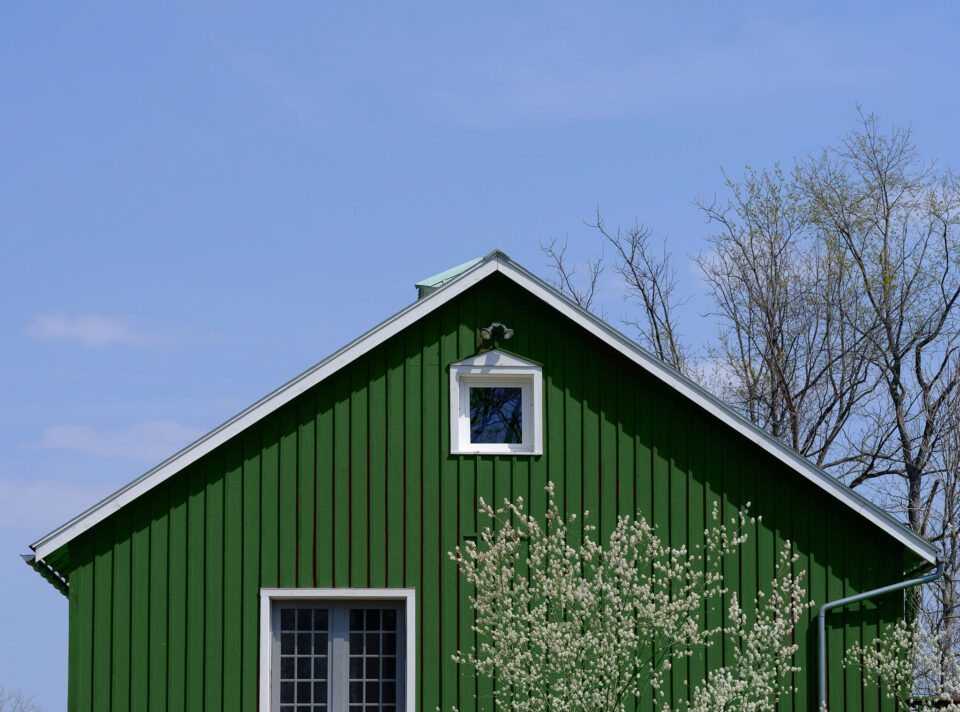

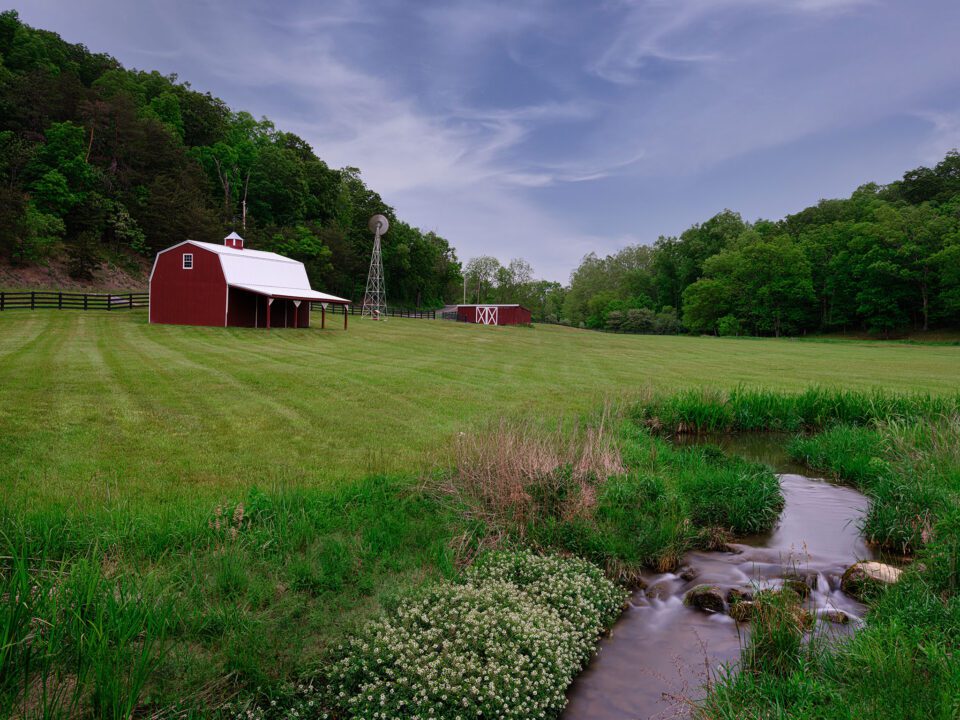
While using the Color Replacement Tool can exist more tedious than either of the above techniques, there are times it is absolutely invaluable. In the image to a higher place, re-coloring the barn where it falls behind the blossoming tree poses quite a challenge. Trying to paint a mask in betwixt those blossoms and branches would be nearly impossible, but the color replacement tool makes this chore fast and like shooting fish in a barrel. It allowed me to paint correct over the unabridged expanse but but affected the pixels that matched the barn color that I had originally sampled.
Conclusion
We have looked at iii ways to supercede color in Adobe Photoshop. The Hue/Saturation Adjustment layer method is unproblematic and extremely flexible, though a bit less flexible than the other methods. The Blending Mode technique is straightforward, but it works all-time on objects that have well-defined edges or on objects that are easy to mask. The third method, using the Color Replacement Brush, is the well-nigh powerful option and is slap-up for more complicated re-coloring that might otherwise crave complicated masking. But it also tends to exist more of a tedious manual method.
There are dozens of ways to practice nigh everything in Photoshop, and these three methods irresolute colors in Photoshop are the ones I find the nigh useful. Other methods exist as well, although about of them utilize some variation or combination of the techniques and tools we looked at today.
There is ane other color alter selection congenital into Photoshop that we did not look at today and that is the Supervene upon Color option located nether Adjustments in the Paradigm menu. Honestly, I take found this tool to be very clunky and I have never managed to utilize it for an effective colour change. Even in images that seemed like they should have been straightforward color replacements, this tool left me with odd blocks of uncolored areas and messy edges. It only didn't exercise a good job. While the lure of what is essentially i click colour replacement might seem tempting, I have never found this tool to alive upwards to its promise and take experienced much better results using the methods described above, even if the process is slightly more tedious.
Also, of class, color replacement isn't always something that photographers are willing to do depending on their style of work. It tin can exist very useful for ad photography, fine fine art compositing, and surreal photos even if y'all don't want to do it to more than straightforward work. But I've likewise found that plenty of everyday photos can benefit from slight colour shifts here and at that place, such equally using the Hue/Saturation tool to isolate an overly cyan sky and go far a bit more bluish.
If you have a dissimilar experience or a different preferred method of color changing, experience costless to share in the comments!
Source: https://photographylife.com/how-to-change-colors-in-photoshop
Posted by: jamesfarinell1998.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Select And Change A Color In Photoshop"
Post a Comment